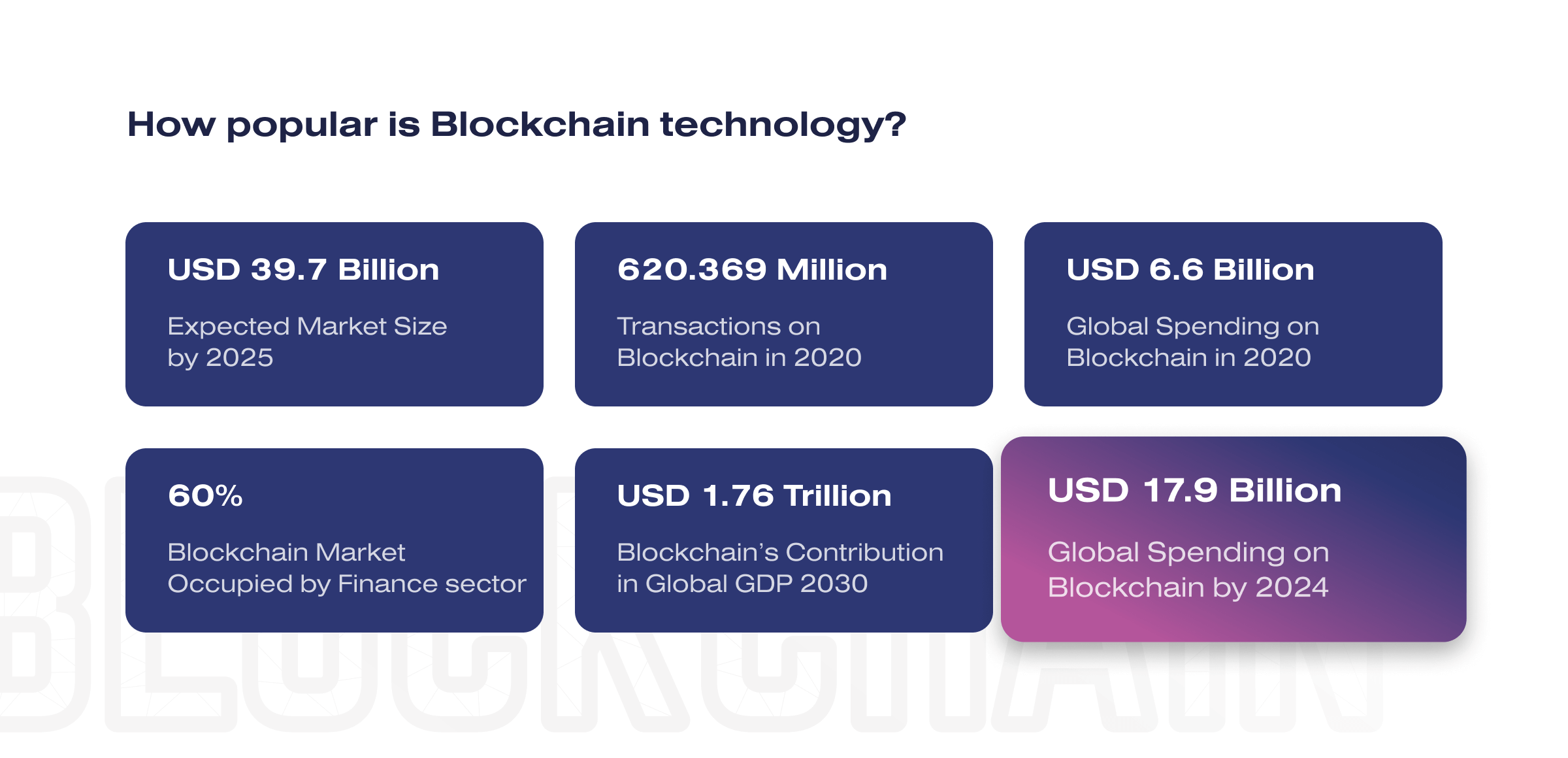
Blockchain is considered by many to be the most significant invention since the Internet’s advent. Some even see it as the innovation driving the fourth industrial revolution. The blockchain industry will develop rapidly, reaching over 39 billion dollars in value by 2025. Today, blockchain is mostly associated with Bitcoin. But cryptocurrencies are only one of many application scenarios for this technology.
In our article, you will find out what blockchain is and how it works. We’ll also analyze the impact of blockchain on e-commerce, real-world use cases, and challenges for blockchain in e-commerce.
Key points
Definition of blockchain technology
Blockchain is about storing and validating data. Avoiding complicated technical nuances and diving into the code level, this technology is easier to understand through analogy.
Imagine that some ledger exists for all people in the world and is synchronized between them. All the information someone enters into that ledger is automatically updated in the entire community. Suppose someone tries to cheat the system by ripping out a page from the ledger or pasting in content with fake numbers. In that case, the algorithm, looking at the data of the other participants, will immediately detect the discrepancy and will not allow it.
Blockchain participants can not deceive each other. Whether they use the blockchain to make a simple financial transaction or choose the president, the mathematics and blockchain algorithms ensure that the underlying data remains intact and unchanged. All transactions are transparent because they are entered into a single database and cannot be tampered with. And blockchain has no governing body – the system is decentralized and self-regulating according to its original rules, which makes it completely predictable.
How does Blockchain work?
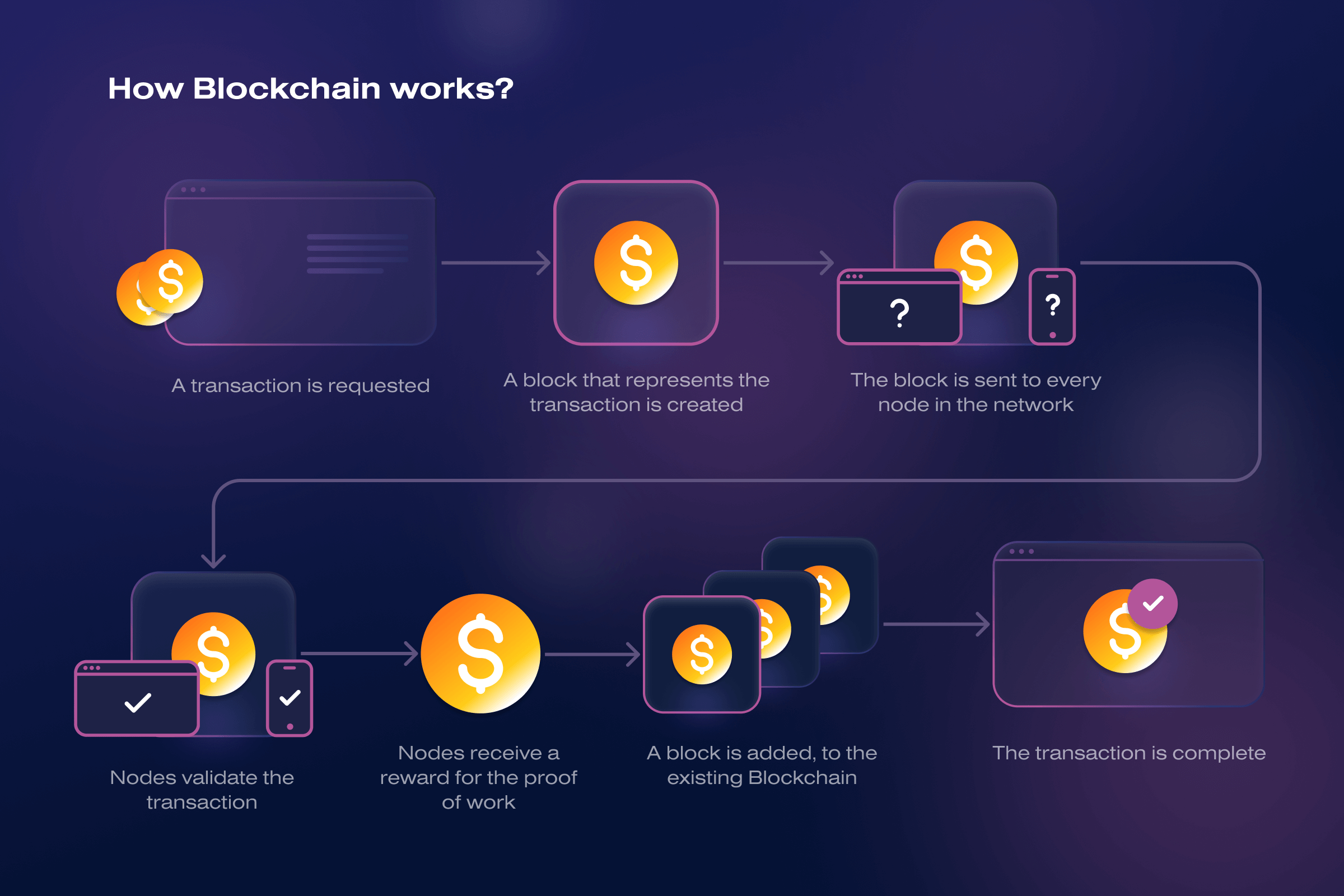
Let’s imagine Alex, who decided to transfer a certain amount of money in cryptocurrency to Mary:
- Transaction. Alex transfers 1 Bitcoin to Mary.
- Encryption. The system encrypts the transaction and places it in a waiting queue.
- Block creation. Computers in the blockchain network (nodes) collect transactions into blocks and send them out to all participants in the blockchain system for verification.
- Block structure. Each block consists of a header and a list of transactions. The header specifies the time the block was created, the hash of that block, and the previous block.
- Hash. According to the network algorithm, the blockchain converts transaction data into a hash sum – a special sequence of 64 characters long. The hash becomes completely different if you change just one character in the data. Therefore, a sequence of linked hashes creates an unbroken chain of blocks.
- Check. Before blocks are added to the chain, they are checked for compliance with the blockchain rules. These rules are called consensus. If there are no errors, each blockchain network member writes a new block to its database.
- Result. The block takes its place in the blockchain. Bitcoin goes from Alex to Mary.
- Built-in protection. Suppose some hacker decided to overwrite one of the blocks. That automatically changes the hash in the block header and all subsequent blocks in the chain. As a result, the nodes find a mismatch and remove the fake block from the blockchain for consensus violation.
As you can see, any data can be reliably stored in blockchain. The key features of blockchain technology include:
- Transparency. All blockchain data is publicly available, meaning anyone can trace the chain of transactions from the beginning of the network’s existence.
- Reliability. Data is stored on multiple users’ computers. This reduces the risks of hacking and computer crashes. Even if dozens of computers fail at once, no information will be compromised.
- Security. The system adds blocks in chronological order and links them by a common hash. Therefore they form an unbreakable chain whose links cannot be deleted or changed.
- Minimal commissions. Instead of centralized intermediaries such as banks, miners log the transactions. Usually, there are a lot of miners, and the competition between them is very high. This keeps the commissions low.
- Independence. There are no intermediaries in the blockchain. Сompanies, banks, and governments cannot interfere in the process.
According to Gartner, blockchain value provided to businesses will hit $176 billion by 2025 and $3.1 trillion by 2030.
Types of blockchain
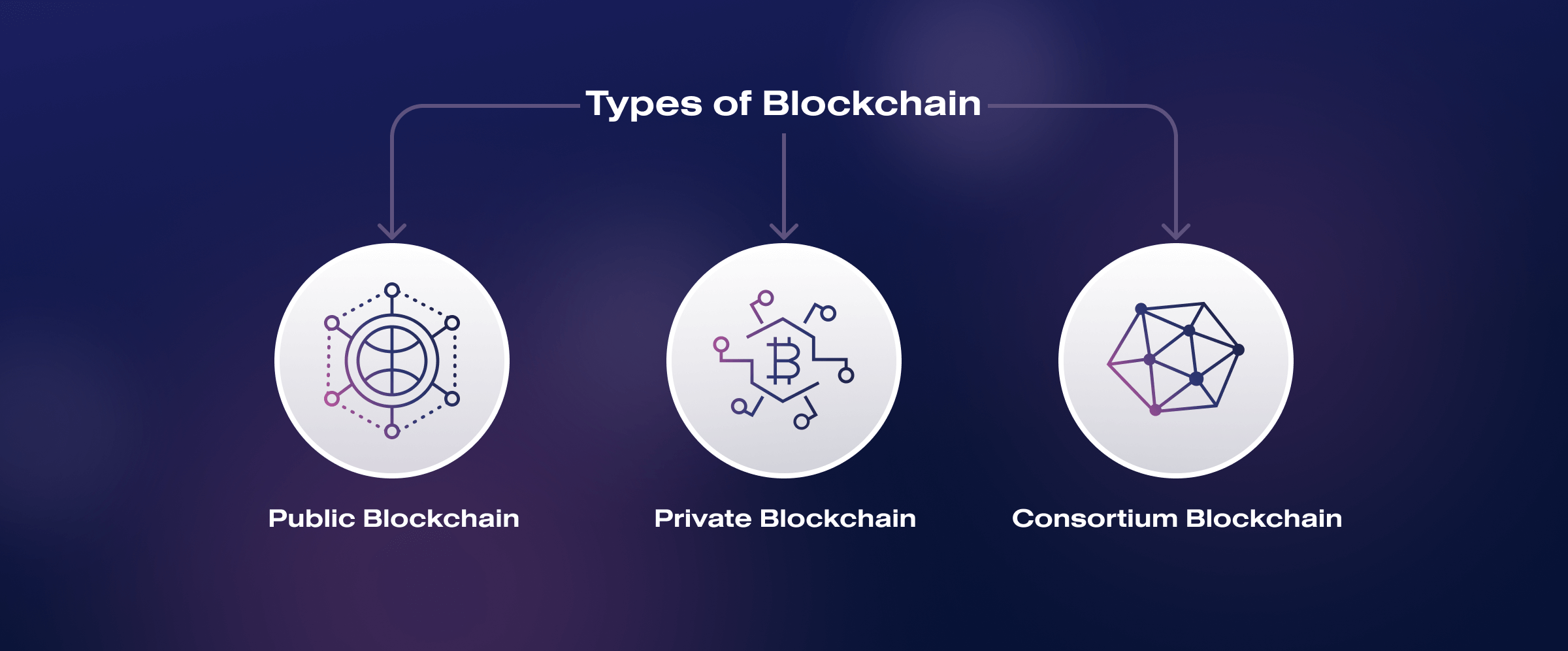
Within blockchain technology, different levels of access to information can be realized. So, different types of blockchains are distinguished:
- Public blockchain. It is fully decentralized or publicly accessible and can be viewed by anyone who installs the necessary program. Anyone is free to join and participate in the network. No one controls transactions. The best-known examples of public blockchains are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Consortium blockchain. It is partially decentralized and consists of some entities that can control the process of matching transactions. The right to view blocks can be publicly available or restricted to a limited number of participants. For a block to be valid, it must be signed by a certain number of consortium members. For example, the Corda R3 blockchain brings together more than 40 major banks for joint bond exchange transactions.
- Private blockchain. It establishes rules whereby a single organization has the right to create blocks. The public can read the information, but only nodes defined by the owners can audit and manage the system. Compared to public blockchains, private blockchains have several advantages: lower transaction cost, higher transaction rate per second, and ease of updating the software part.
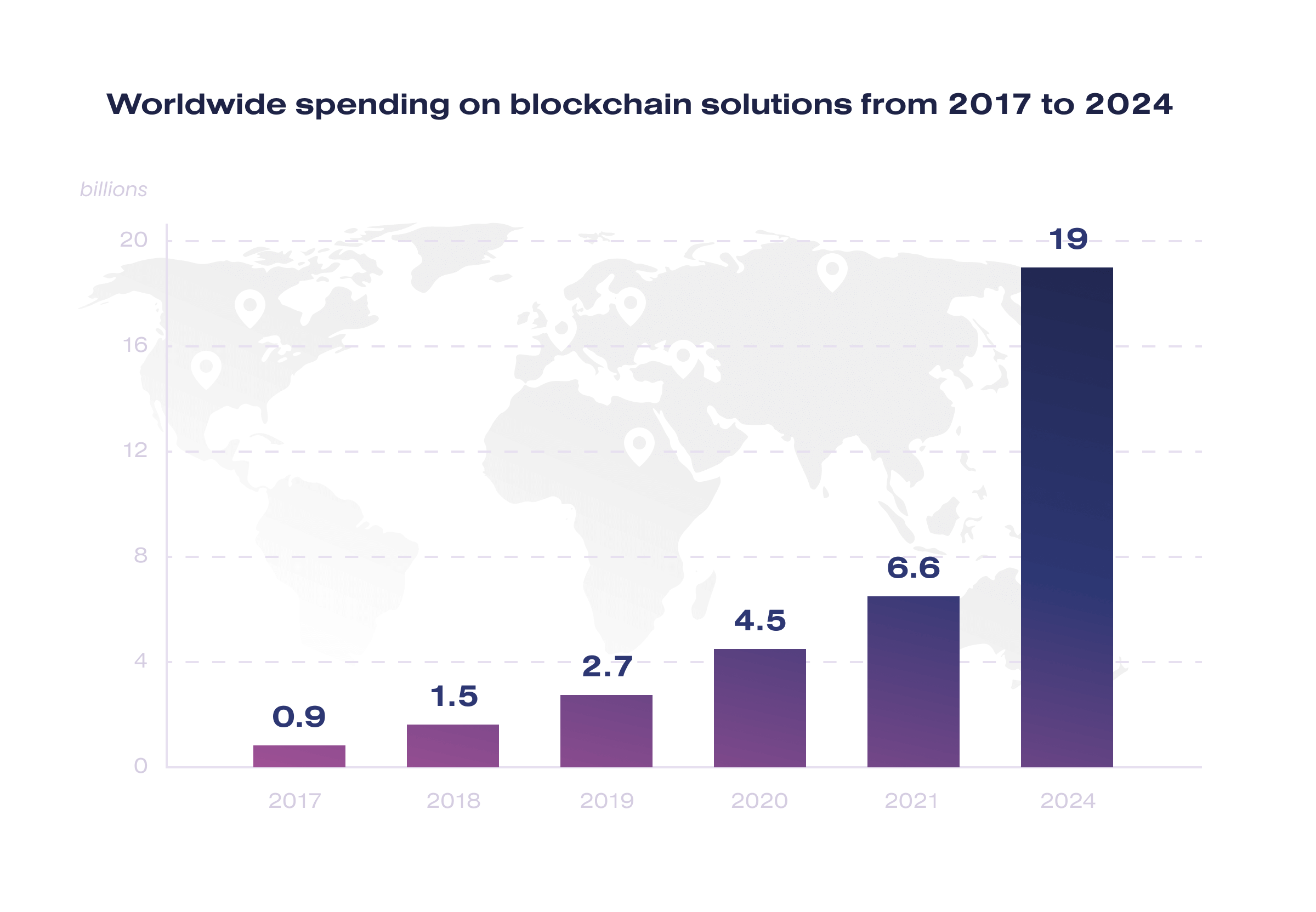
According to the IDC report, the banking industry invested the most in blockchain (29.7%) in 2020. Other significant investments were made by manufacturing (11.4%), discrete manufacturing (10.9%), professional services (6.6%), and retail (6%).
Impact of blockchain on e-commerce
Statistics that indicate major e-commerce issues and stop its growth:
- Fraud will cost e-commerce merchants $343 billion over the next 5 years
- 14.6% of phishing attacks globally during the first quarter of 2022 targeted the retail and eCommerce sectors.
- 7 out of 10 online buyers will abandon a purchase due to exorbitant delivery prices.
- Just 34% of customers indicate that delivery procedures have become better.
One of the blockchain missions is to change e-commerce. The introduction of blockchain-based eCommerce platforms will allow the seller and the buyer to interact directly. Affordable threshold of entry into business due to cheaper logistics, lack of monopoly, higher customer data security, and some other changes will impact e-commerce significantly.
Real-world examples of blockchain in e-commerce
Real-world examples of blockchain in e-commerce include:
- OpenBazaar
- Blockpoint.io
- Loyyal
- ShopIN
- Buying.com
Companies like Nestlé, Maersk, Amazon, and IBM are already adopting blockchain for e-commerce purposes. Now let`s discuss 3 of the most beneficial blockchain applications.
In payment systems
The most obvious area of using blockchain benefits in e-commerce is payments. Today’s payment systems, despite their efficiency, are far from perfect. The more global the e-commerce market becomes, the more obvious these shortcomings become. Current payment processors such as PayPal or Payoneer charge a fee (2-3%) for using their platform.
Blockchain allows for fast, secure, and cheap transfers, as has been successfully proven by projects such as Request Network. As such solutions proliferate in eCommerce, financial transactions will become cheaper, and large payment system players will lose the right to a monopoly. Any e-commerce business model will be able to function with minimal transaction fees.
Implementations in marketplaces
An important challenge today is the protection of personal data. Marketplaces store all information on their servers, including customers’ banking information. In this format, they are vulnerable to hackers. It is obvious that the Internet infrastructure in its current form has many vulnerabilities.
The security advantage of blockchain is mainly the absence of a centralized data storage system. It is impossible to attack all the decentralized nodes of a blockchain platform. Information cannot be stolen, altered, or deleted because all information is encrypted. Strong cryptography and additional security mechanisms are used to ensure the highest standards of security.
Integration with logistics and shipping
Effective supply chain and inventory management are key aspects of e-commerce. This market is already facing logistical challenges that are difficult to solve with traditional tools because of its growth dynamics.
Transparency and security of blockchain can change logistics and shipping. Blockchain-based solutions enable the tracking of shipments at all stages of their movement. At any stage, an object can be monitored while its history verified. All this allows us to bring logistics to a new level, reduce costs, eliminate the corruption component, and eliminate third parties.
A primary example is the VeChain project. On the VeChain platform, a personal identifier is assigned to an item, which is sent to the blockchain and simultaneously placed on the item itself using an NFC chip, RFID tag, or QR code. These devices allow goods to be tracked at any stage of their logistic cycle. By comparing the information on the identifier with the manufacturer’s database, it is possible to check the product for authenticity. This solves the problem of counterfeit goods.
Challenges and limitations of blockchain in e-commerce

Despite the wonderful benefits of blockchain technology, there are also shortcomings. Challenges (they are limitations) that need to be addressed when implementing blockchain in e-commerce:
- Low scalability. Transaction speed depends on network congestion.
- Implementation challenge. Implementation costs may be overwhelming.
- Private key issues. They provide access to all the data stored. If a private key is stolen, sensitive data and finances are at risk.
- Problematic integration with legacy systems. Integrating blockchain solutions with outdated systems can cause data loss and corruption risks.
Blockchain can cause temporary e-commerce business disruptions because of its limitations. Therefore, it’s crucial to introduce it wisely and with the high-skilled e-commerce software team.
Conclusion
Humanity has not faced such a powerful and versatile technology for a long time. Blockchain has the potential to affect all sectors of the economy and change the way we think about serving our needs in general. We are already witnessing how blockchain technology penetrates and effectively transforms various areas.





